SPOT-peptide: Information

Key terms:
Query: The name of the query structure.
Sites: The number of non-redundant predicted binding sites for the query protein (MCC<0.3).
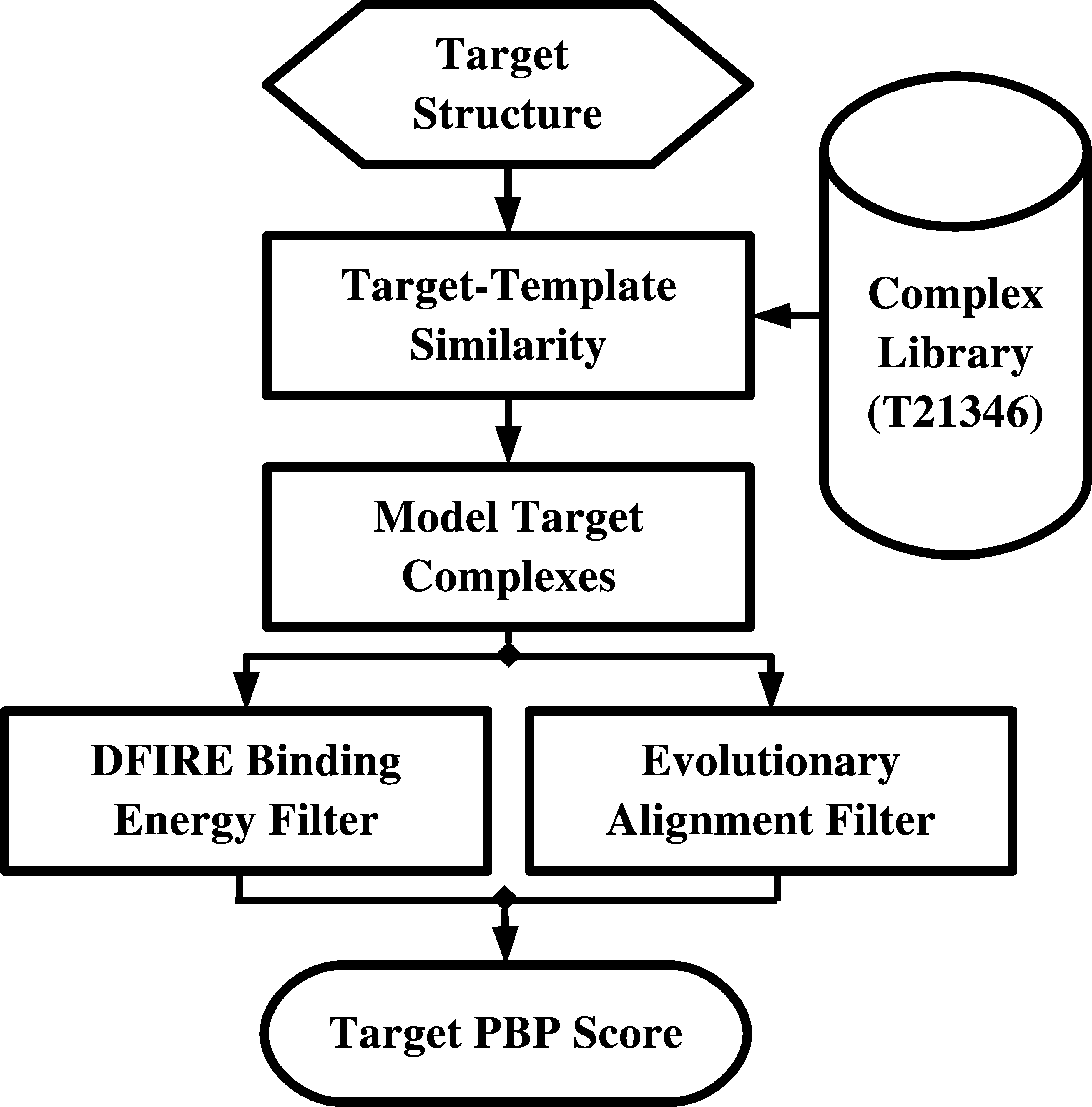
SP-score: The measure of domain-level structural similarity between the query and top-scoring template.
TPL: The PDB chain ID of the top-scoring template protein.
TPL-peptide: The BioLiP ID of the peptide associated with the top-scoring template.
Cluster size: The number of redundant templates which imply the diven predicted binding site.
DFIRE: The interface energy between the query protein and superimposed template peptide normalised by peptide length (lower better).
EVO: Mean sequence similarity between query-template aligned residues in the putative binding region (higher better).
Residues: The predicted binding residues (based on original query PDB numbering).